Flagship topics
Control of CAR T cells and management of side effects
CAR T cells are "living drugs" that require technologies to enable physicians (and patients) to maintain control over the infused cell product. Therefore, the Hudecek Lab develops several strategies to gain direct control over CAR T cells after injection. The Tyrosine kinase inhibitor Dasatinib has been shown to be highly effective in regulating CAR T cell acitivity in a dose dependent manner in vitro and in vivo and is being incorporated as a safety switch into several clinical trials. Additionally, the Hudecek lab evaluates the regulation of CAR T cells a) at different steps of receptor signalling, and b) the use of conventional and innovative lymphodepletion strategies for improved management of CAR T related toxicities.
Publications
Mestermann K, Rydzek J, Frenz S, Nerreter T, Mades A, Einsele H, Hudecek M. Sci Transl Med. (2019)
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib acts as a pharmacologic on/off switch for CAR-T cells. 2019 Jul 3;11(499).
New targets for CAR T cell therapy
Generating safe CAR T cells against new targets is a major focus of the Hudecek Lab. This includes the preclinical development of a CAR, starting with receptor design, the functional characterization in vitro and in vivo, and the clinical evaluation of promising candidates. Recently, the Hudecek lab has developed CARs targeting different targets for solid and hematological cancers.
Publications
Jetani H*, Navarro-Bailón A*, Maucher M*, Frenz S, Verbruggen CM, Yeguas A, Vidriales M-B, González M, Rial Saborido J, Kraus S, Mestermann K, Thomas S, Bonig H, Luu M, Monjezi R, Mougiakakos D, Sauer M, Einsele H, Hudecek M (*shared first authorship) (2021)
Siglec-6 is a novel target for CAR T-cell therapy in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Blood.
Gogishvili T, Danhof S, Prommersberger S, Rydzek J, Schreder M, Brede C, Einsele H, Hudecek M. (2017)
SLAMF7-CAR T cells eliminate myeloma and confer selective fratricide of SLAMF7+ normal lymphocytes.
Blood. 2017 Dec 28;130(26):2838-2847. Epub 2017 Oct 31.
Additional reviews
Fabian Freitag, Marius Maucher, Zeno Riester, Michael Hudecek (2020)
New targets and technologies for CAR-T cells.
Curr Opin Oncol. 2020 Sep;32(5):510-517.
Go to publication
Improving CAR T manufacturing
The production of CAR T cells requires several carefully performed steps that are complex, expensive and the entire process until delivery of the targeted CAR-T product can take too long time compared to the needs of the patients. Therefore, the Hudecek lab is striving to optimize and shorten the production of CAR T cells. Hereby, we focus on virus free genome editing techniques and targeted gene delivery to make CAR T cell production, more efficient, safe and reliable. In cooperation with industry partners, we are evaluating the potential of fully automated manufacturing platforms to produce clinical grade CAR T cells.
Publications
Querques I, Mades A, Zuliani C, Miskey C, Alb M, Grueso E, Machwirth M, Rausch T, Ivics Z, Hudecek M*, Barabas O * (*shared last authorship) (2019)
A highly soluble Sleeping Beauty transposase improves control of gene insertion.
Nature Biotechnology 37, 1502–1512.
Improving CAR T cell function
CAR T cell therapy has been highly promising when targeting hematologic malignancies, however, there are settings in which CAR T cell function can be optimized. Therefore, the Hudecek Lab is aiming to improve CAR T cell functions, e.g. by evaluating and targeting resistance mechanism that CAR T cells face in the immunosuppressive microenvironment of solid cancer. Thereby, we will hopefully be able to protect CAR T cells from said environment and drive forward the targeting of solid malignancies. Additionally, we focus on the fine-tuning of CAR sensitivity and signalling to achieve a highly balanced CAR T cell function.
Publications
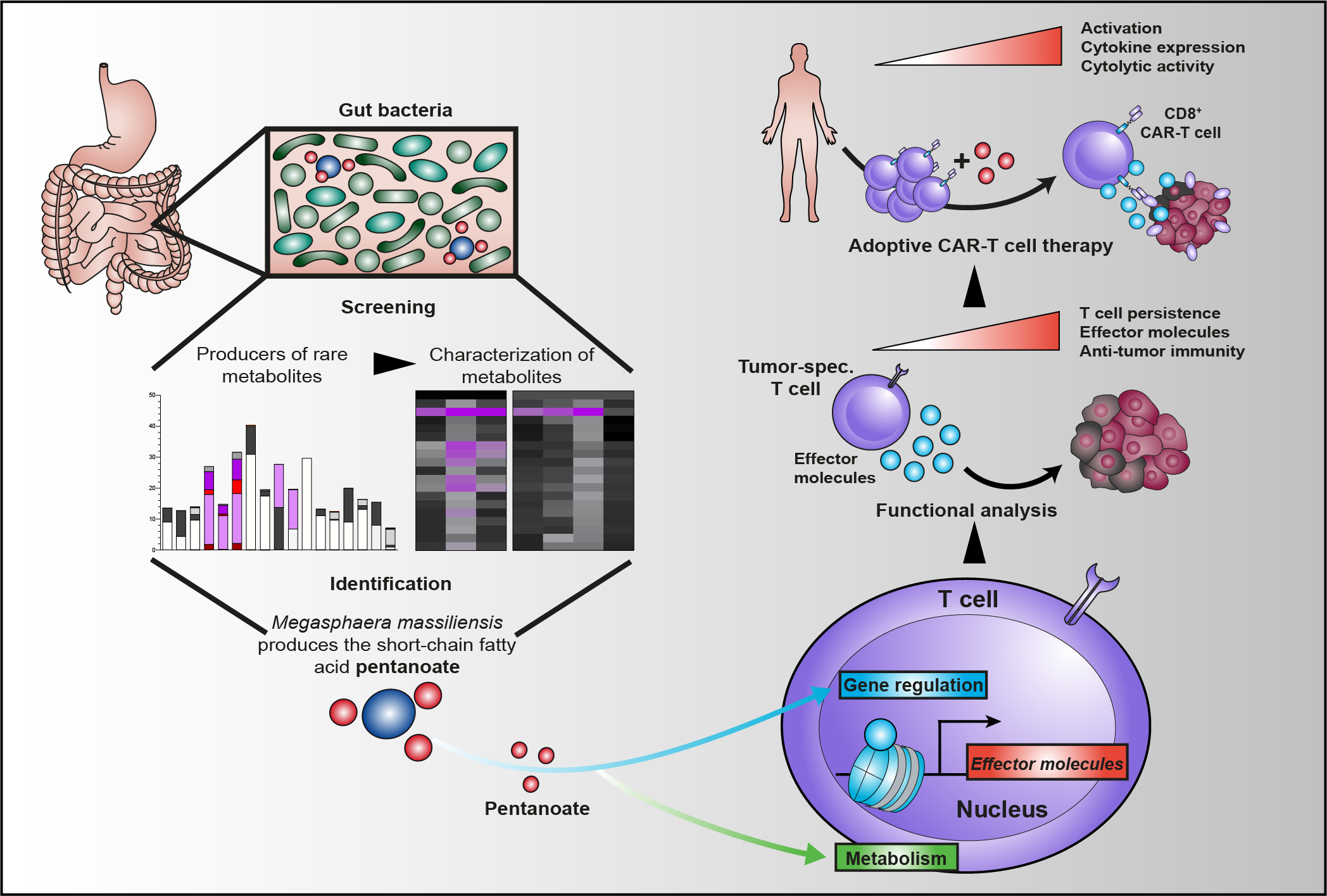
Luu M, Riester Z, Baldrich A, Reichardt N, Yuille S, Busetti A, Klein M, Wempe A, Leister H, Raifer H, Picard F, Muhammad K, Ohl K, Romero R, Fischer F, Bauer CA, Huber M, Gress TM, Lauth M, Danhof S, Bopp T, Nerreter T, Mulder IE, Steinhoff U, Hudecek M*, Visekruna A* (*shared last authorship) (2021)
Microbial short-chain fatty acids modulate CD8+ T cell responses and improve adoptive immunotherapy for cancer.
Nat Commun 12:4077.
Gudipati V*, Rydzek J*, Doel-Perez I, Goncalves V, Scharf L, Königsberger S, Lobner E, Kunert R, Einsele H, Stockinger H, Hudecek M**, Huppa J**. (*shared first authorship; **shared correspondence) (2020)
Inefficient CAR-proximal signaling blunts antigen sensitivity.
Nat Immunol 21, 848–856.
New technologies
By exploring new technologies, we aim to widen the limits for CAR T cell therapy. For many decades, CAR T cells were produced in a very similar way – virus-based approaches that evaluate one design at a time. We think it is time to think outside of the box! Therefore, the Hudecek Lab has established and is further developing Virus-free gene transfer systems that can also be used to approach new designs by screening complex CAR-libraries. For the same amount of time, the detection limit of target antigen on the tumor surface that can be recognized by a CAR has been unknown. By using high resolution microscopy, we define new borders of antigen expression that enable the treatment of patients that have been previously characterized as non-expressors and thus have been doomed unsuitable for CAR Therapy.
Publications

Sleeping beauty transpospon system
Hudecek M, Ivics Z. (2018)
Non-viral therapeutic cell engineering with the Sleeping Beauty transposon system.
Curr Opin Genet Dev., 2018 Oct; 52:100-108. Epub 2018 Oct 12.
Super-resolution microscopy
Nerreter T, Letschert S, Götz R, Doose S, Danhof S, Einsele H, Sauer M, Hudecek M. Nat Commun. (2019)Super-resolution microscopy reveals ultra-low CD19 expression on maeloma that triggers elimination by CD19 CAR-T.2019 Jul 17;10(1):3137.
Microphysiological models
Wallstabe L, Göttlich C, Nelke LC, Kühnemundt J, Schwarz T, Nerreter T, Einsele H, Walles H, Dandekar G, Nietzer SL, Hudecek M. (2019)ROR1-CAR T cells are effective against lund and breast cancer in advanced microphysiologic 3D tumor models.JCI Insight. 2019;4(18):e126345.
Additional reviews
Luu M, Visekruna A (2021)
Microbial metabolites: novel therapeutic tools for boosting cancer therapies.
Trends in Cell Biology.
Go to publication
Arcangeli S, Mestermann K, Weber J, Bonini C, Casucci M, Hudecek M. (2020)
Overcoming key challenges in cancer immunotherapy with engineered T cells.
Current Opinion in Oncology. 32. 398-407.
Go to publication
Kansagra AJ, Frey NV, Bar M, Laetsch TW, Carpenter PA, Savani BN, Heslop HE, Bollard CM, Komanduri KV, Gastineau DA, Chabannon C, Perales MA, Hudecek M, Aljurf M, Andritsos L, Barrett JA, Bachanova V, Bonini C, Ghobadi A, Gill SI, Hill J, Kenderian S, Kebriaei P, Nagler A, Maloney D, Liu HD, Shah NN, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Shpall EJ, Mufti GJ, Johnston L, Jacoby E, Bazarbachi A, DiPersio JF, Pavletic SZ, Porter DL, Grupp SA, Sadelain M, Litzow MR, Mohty M, Hashmi SK. (2018)
Clinical Utilization of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: An Expert Opinion from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant., 2019 Mar;25(3):e76-e85.
Go to publication
Köhler M, Greil C, Hudecek M, Lonial S, Raje N, Wäsch R, Engelhardt M. Cancer. (2018)
Current developments in immunotherapy in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Feb 6. [Epub ahead of print] Review.
Go to publication