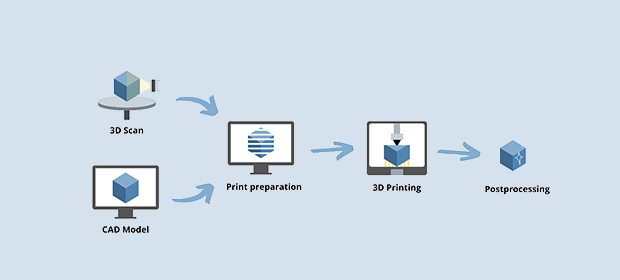
3D scanning and 3D printing
We describe here the 3D scanning and printing pipeline that we have set up at InExEn in order to develop various different prototypes.
3D Scanning
3D scanning is a process in which an object is analyzed and data about its shape and appearance is collected. The collected data is then used to reconstruct the object as a 3D model.
To do this, we use a Shining 3D EinScan Pro 2X scanner together with the EinScan Industrial and Color packs.
CAD modeling
We mainly use Siemens Solid Edge to create, edit, and analyze 3D models, as it has many features that are helpful with 3D scanning and 3D printing.
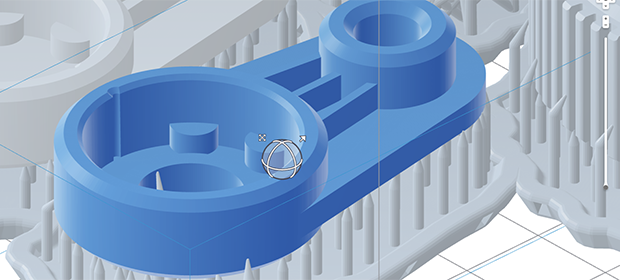
Print preparation
Before the models are sent to printing they are processed by additional tools provided by the 3D printers manufacturers.
3D printing
At InExEn, we have three different 3D printers with unique printing technologies:
- Stereolithography (SLA) – FormLabs 3B: a method that is able to produce biocompatible, highly accurate parts that are flexible or rigid.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – Sinterit Lisa Pro: a method that is able to produce many parts simultaneously, with good mechanical properties and surface quality.
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) – Ultimaker 2+: a method that is good for fast production of prototypes made of many different polymers (PLA, ABS, PC, etc.).
Postprocessing
Once the part is fully printed and removed from the printer, some additional steps are required before it is ready for use. Depending on the 3D printing method, parts need to be washed, cured, cleaned, brushed, or separated from supporting structures.